Why are ecosystems important?

Ecosystems make up our planet. All life is part of an ecosystem, and ecosystems are interconnected. Damaging a part of an ecosystem can lead to a collapse, and the state of one ecosystem can have effects on nearby systems.
Ecosystem services are resources, functions, and intrinsic value provided by an ecosystem that can contribute directly or indirectly to our social welfare and impact our survival and quality of life. We can benefit from them when we sustainably maintain a variety of ecosystems.
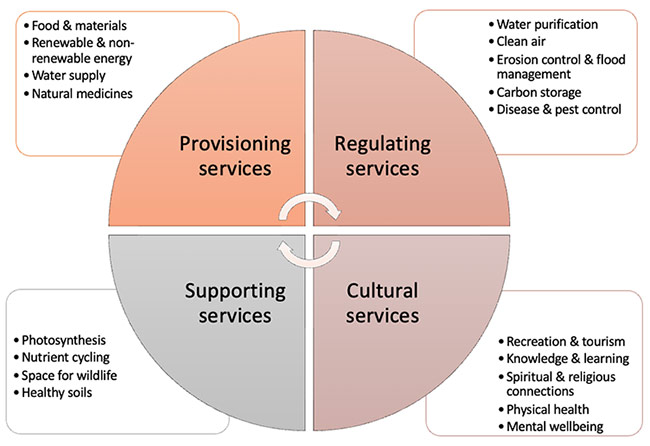
There are four types of ecosystem services:
- Provisioning services: Tangible goods that we can obtain from the ecosystem like food, freshwater, raw materials (such as wood, biofuels and plant oils) and medicinal resources.
- Regulating services: Benefits provided by ecosystems processes and functions to regulate natural phenomenon. This includes climate and air quality, carbon storage, flood management, water filtration and more.
- Supporting services: The underlying natural processes, like photosynthesis, nutrient cycling, the creation of soils and the water cycle, which play a significant role in maintaining ecosystems.
- Cultural services: Intangible benefits that impact people's health and well-being. These include recreation, educational opportunities, spiritual enrichment and aesthetic values. Studies have shown that nature positively affects our health and well-being.
Many crucial ecosystem services are provided by the living organisms which inhabit the ecosystem. Since all of these organisms are connected, each one plays a role in the balance of the system and the loss of even one species risks shifting the dynamics of the community.
Higher diversity of communities, species, and genes increase overall ecosystem resilience (the capacity of an ecosystem to respond, resist, and recover from damage and disturbances).
Connecting biodiversity and conservation to the UN SDGs
Conserving biodiversity is critical to meeting the UN Sustainable Development Goals.
1: No poverty

- A healthy ecosystem can provide available resources that may be gathered, such as water, edible and medicinal plants, animals and firewood.
- Having locally available resources contributes to a higher standard of living and reduced health problems.
- Preserving biodiversity is crucial for generating resources and income for many communities, particularly the rural poor.
- By adopting ecosystem-based sustainable agriculture, protecting, and restoring ecosystems, we can prevent poverty and improve the community’s financial stability. This approach can increase income and reduce vulnerability to economic shocks and environmental disasters.
2: Zero hunger

- Crops are more resilient when they have a diversity of genes to allow them to adapt to changing conditions. Genetically modified crops have a very low amount of genetic diversity, and are susceptible to diseases, pests and the effects of changes in climate.
- Over one third of global food production depends at least in part on animal pollinators, which depend on multiple other ecosystem factors. This is just one of the many ecosystem functions that influence food availability.
- Preserving biodiversity contributes to food security, decreasing the likelihood of market fluctuations or failures.
- Companies may have control over the sale and usage of genetically modified organisms, giving them power over disadvantaged farmers.
- Many people depend on food gathered from local ecosystems.
13: Climate action

- Protecting carbon-sequestering ecosystems, such as forests, helps to slow global warming.
- Preserving a diversity of ecosystems, species and genes is crucial to adapting to climate change. As species go extinct or are extirpated, it is important to fill those ecological niches.
- Maintaining connected habitat patches is important to the conservation of many species, as they will need a corridor to migrate through as the climate changes.
- Climate action is a part of conservation efforts, as the changing climate puts many species at risk.
14: Life below water

- Marine species provide many of the same benefits as those that are terrestrial. Roughly half of earth’s oxygen production comes from oceanic plankton.
- A diversity of life ensures the survival and abundance of food resources, which are necessary for many communities, including small island nations which are at particular risk from the impacts of climate change.
- Marine and aquatic ecosystems are complex, and in many ways mysterious. With so many cryptic species, it is important to address threats proactively.
- The wonders and beauty of marine biodiversity have an intrinsic value.
15: Life on land

- The abundance of life on earth depends on having a wide array of healthy ecosystems; losing just one type of environment could lead to the loss of species which depend on it.
- Ecosystem services provided by terrestrial species are some of the most accessible for human use. Being land animals ourselves, humans can farm and grow many resources, but not without the influence of other species (e.g., pollinators, decomposers in soil, etc.).
- The abiotic factors of land that impact our lives are heavily influenced by biotic factors. Trees and other vegetation protect the structure of our soil, the quality of our water and air and even the local temperature.
- There is intrinsic value to biodiverse earth ecosystems, which benefit not only physical health, but mental health as well.
Did you know?
In 2022, the UN reported that approximately 1 million animal and plant species are presently threatened with extinction. How important is this statistic? While the true number of species on earth is unknown, the number that have been described is under 2 million. That means that one for every two species that you have ever heard of is threatened.
Check your understanding
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.

